Khan Academy on a Stick
Thermodynamics
-
 Thermodynamics (part 1)
Thermodynamics (part 1)
Intuition of how gases generate pressure in a container and why pressure x volume is proportional to the combined kinetic energy of the molecules in the volume.
-
 Thermodynamics (part 2)
Thermodynamics (part 2)
Example problem that pv=pv. Introduction to temperature.
-
 Thermodynamics (part 3)
Thermodynamics (part 3)
Introduction to Kelvin. Example of a problem involving the ideal gas law
-
 Thermodynamics (part 4)
Thermodynamics (part 4)
Introduction to the concept of a mole. Universal gas constant R. PV=nRT
-
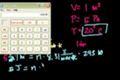 Thermodynamics (part 5)
Thermodynamics (part 5)
Example problem involving PV=nRT
-
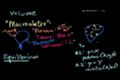 Macrostates and microstates
Macrostates and microstates
The difference between macrostates and microstates. Thermodynamic equilibrium.
-
 Quasistatic and reversible processes
Quasistatic and reversible processes
Using theoretically quasi-static and/or reversible processes to stay pretty much at equilibrium.
-
 First law of thermodynamics / internal energy
First law of thermodynamics / internal energy
First law of thermodynamic and Internal Energy
-
 More on internal energy
More on internal energy
Getting more intuition of internal energy, heat, and work
-
 Work from expansion
Work from expansion
How a system can do work by expanding
-
 Pv-diagrams and expansion work
Pv-diagrams and expansion work
Why work from expansion is the area under the curve of a PV-diagram
-
 Proof: U = (3/2)PV or U = (3/2)nRT
Proof: U = (3/2)PV or U = (3/2)nRT
Conceptual proof that the internal energy of an ideal gas system is 3/2 PV.
-
 Work done by isothermic process
Work done by isothermic process
Isothermic and Adiabatic processes. Calculating the work done by an isothermic process. Seeing that it is the same as the heat added.
-
 Carnot cycle and Carnot engine
Carnot cycle and Carnot engine
Introduction to the Carnot cycle and Carnot heat engine
-
 Proof: Volume ratios in a carnot cycle
Proof: Volume ratios in a carnot cycle
Proof of the volume ratios in a Carnot Cycle
-
 Proof: S (or entropy) is a valid state variable
Proof: S (or entropy) is a valid state variable
Proof that S (or entropy) is a valid state variable.
-
 Thermodynamic entropy definition clarification
Thermodynamic entropy definition clarification
Clarifying that the thermodynamic definition of Entropy requires a reversible system.
-
 Reconciling thermodynamic and state definitions of entropy
Reconciling thermodynamic and state definitions of entropy
Long video explaining why entropy is a measure of the number of states a system can take on (mathy, but mind-blowing).
-
 Entropy intuition
Entropy intuition
A discussion of what entropy is and what it isn't.
-
 Maxwell's demon
Maxwell's demon
Maxwell's Demon: A thought experiment that seems to defy the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
-
 More on entropy
More on entropy
More clarification as to what entropy is and what entropy is not.
-
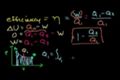 Efficiency of a Carnot engine
Efficiency of a Carnot engine
Definition of efficiency for a heat engine. Efficiency of a Carnot Engine.
-
 Carnot efficiency 2: Reversing the cycle
Carnot efficiency 2: Reversing the cycle
Seeing how we can scale and or reverse a Carnot Engine (to make a refrigerator)
-
 Carnot efficiency 3: Proving that it is the most efficient
Carnot efficiency 3: Proving that it is the most efficient
Proving that a Carnot Engine is the most efficient engine
-
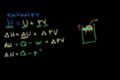 Enthalpy
Enthalpy
Understanding why enthalpy can be viewed as "heat content" in a constant pressure system.
-
 Heat of formation
Heat of formation
Standard heat of formation or standard enthalpy change of formation.
-
 Hess's law and reaction enthalpy change
Hess's law and reaction enthalpy change
Using Hess's Law and standard heats of formation to determine the enthalpy change for reactions
-
 Gibbs free energy and spontaneity
Gibbs free energy and spontaneity
Intuition behind why spontaneity is driven by enthalpy, entropy and temperature. Introduction to Gibbs free energy.
-
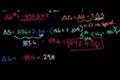 Gibbs free energy example
Gibbs free energy example
Determining if a reaction is spontaneous by calculating the change in Gibbs Free Energy.
-
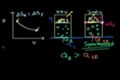 More rigorous Gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship
More rigorous Gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship
More formal understanding of why a negative change in Gibbs Free Energy implies a spontaneous, irreversible reaction.
-
 A look at a seductive but wrong Gibbs/spontaneity proof
A look at a seductive but wrong Gibbs/spontaneity proof
A look at why the "proof" of the relation between changes in Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity is wrong in many textbooks.
-
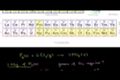 Stoichiometry example problem 1
Stoichiometry example problem 1
Figuring grams of reactants and product produced from reaction of phosphorous and chlorine.
-
 Stoichiometry example problem 2
Stoichiometry example problem 2
-
 Limiting reactant example problem 1
Limiting reactant example problem 1
Limiting Reactant Example Problem 1
-
 Empirical and molecular formulas from stoichiometry
Empirical and molecular formulas from stoichiometry
Empirical and Molecular Formulas from Stoichiometry
-
 Example of finding reactant empirical formula
Example of finding reactant empirical formula
Example of Finding Reactant Empirical Formula
-
 Stoichiometry of a reaction in solution
Stoichiometry of a reaction in solution
Stoichiometry of a Reaction in Solution
-
 Another stoichiometry example in a solution
Another stoichiometry example in a solution
Another Stoichiometry Example in a Solution
-
 Molecular and empirical formulas from percent composition
Molecular and empirical formulas from percent composition
Molecular and Empirical Forumlas from Percent Composition. Example 2.9 from Kotz Chemistry book
-
 Hess's law example
Hess's law example
Hess's Law Example
